RD Calculator
RD Calculator: Your Ultimate Guide to Smart Savings
In the world of personal finance, consistency is key. If you’re someone who prefers to save a fixed amount regularly, a Recurring Deposit (RD) is an excellent choice. But how do you know how much your monthly savings will grow over time? That’s where an RD calculator comes in. This tool helps you estimate the maturity amount of your RD, making financial planning a breeze.
What is an RD Calculator?
An RD calculator is an online tool that helps you compute the maturity amount of your recurring deposit. By inputting details like your monthly deposit amount, interest rate, and tenure, the calculator provides an estimate of how much you’ll have at the end of your investment period.
How Does an RD Calculator Work?
The RD calculator uses a formula that takes into account:
Monthly Deposit (P): The fixed amount you contribute every month.
Interest Rate (r): The annual interest rate offered by the bank.
Tenure (n): The duration of the deposit, typically in months.
Table of Contents
The formula for calculating the maturity amount is:
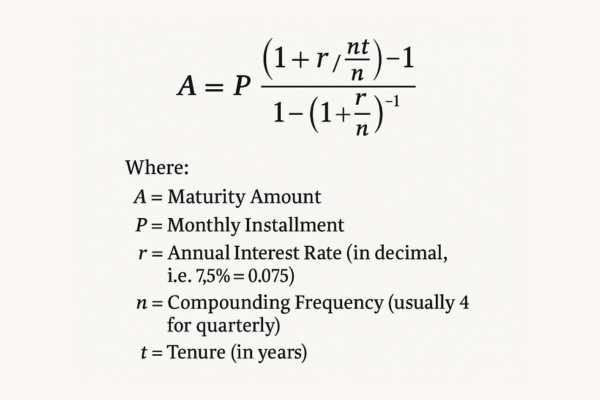
Why Should You Use an RD Calculator?
Using an RD calculator offers several benefits:
- Accurate Projections: Get precise estimates of your maturity amount.
- Financial Planning: Helps in budgeting and setting realistic financial goals.
- Comparison Tool: Compare different RD schemes to find the best fit for you.
- Time-Saving: Quickly calculate returns without manual calculations.
RD Calculator: A Step-by-Step Guide Using an RD calculator is straightforward
- nter Monthly Deposit: Input the amount you plan to save each month.
- Select Interest Rate: Choose the interest rate offered by your bank.
- Set Tenure: Decide the duration of your RD.
- Calculate: Hit the calculate button to see your estimated maturity amount.
Factors Affecting RD Returns Several factors can influence your RD returns
- Interest Rate: Higher rates yield better returns.
- Tenure: Longer tenures typically offer higher rates.
- Compounding Frequency: Quarterly compounding can lead to higher returns than monthly compounding.
- Taxation: Interest earned on RDs is taxable, which can affect your net returns.
Tips to Maximize RD Returns To get the most out of your RD:
- Choose Longer Tenures: Longer durations often come with higher interest rates.
- Avoid Premature Withdrawals: Withdrawing before maturity can lead to penalties and reduced interest.
- Compare Banks: Different banks offer varying interest rates; shop around to find the best deal.
- Regular Deposits: Ensure timely monthly deposits to avoid penalties.
[posts_table]
🧾 Reccuring Deposit Calculator FAQs
Q1: Is TDS applicable on RD?
Yes, Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is applicable on RD interest if it exceeds ₹40,000 in a financial year (₹50,000 for senior citizens). The TDS rate is 10% .
Q2: Can I withdraw my RD before maturity?
Yes, but premature withdrawal may attract penalties, and the interest rate may be reduced. It’s advisable to check with your bank for specific terms .
Q3: Is RD interest taxable?
Yes, the interest earned on RD is taxable as per your income tax slab. You can submit Form 15G/15H if your total income is below the taxable limit to avoid TDS .
🧾 RD Calculator FAQs
Q1: Is TDS applicable on RD?
Yes, Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is applicable on RD interest if it exceeds ₹40,000 in a financial year (₹50,000 for senior citizens). The TDS rate is 10% .
Q2: Can I withdraw my RD before maturity?
Yes, but premature withdrawal may attract penalties, and the interest rate may be reduced. It’s advisable to check with your bank for specific terms .
Q3: Is RD interest taxable?
Yes, the interest earned on RD is taxable as per your income tax slab. You can submit Form 15G/15H if your total income is below the taxable limit to avoid TDS .
📝 Conclusion
An RD calculator is an invaluable tool for anyone looking to plan their savings effectively. By providing accurate estimates of your maturity amount, it helps you make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals. Remember to consider factors like interest rates, tenure, and taxation to maximize your returns.







